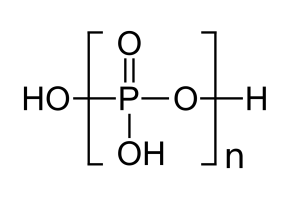
Application of Polyphosphoric Acid:
Application of Polyphosphoric acid. Polyphosphoric acid is a protonic acid, which can dissolve a variety of low molecular and high molecular organic compounds. Used as a catalyst or solvent for condensation, cyclization, rearrangement, substitution and other reactions. Used as a compound cyclizing agent and acylating agent in organic synthesis. Also used as a substitute for orthophosphoric acid and analytical reagents.
Polyphosphoric acid (PPA) has strong dehydration, low nucleophilicity and moderate acidity. Unlike sulfonic acid, polyphosphoric acid generally does not oxidize reactants and is soluble in organic solvents. Although its acidity is weaker than sulfonic acid, its dehydration property is equivalent to 100% sulfonic acid, so it is widely used in laboratories. . [3] Catalytic intramolecular cyclization reaction Polyphosphoric acid can catalyze the intramolecular cyclization reaction of carboxylic acids, esters, ketones, aldehydes, alcohols, alkenes and hydrazones [1], such as the synthesis of quinone under the catalysis of PPA (formula 1)
Many quinolines and quinoline derivatives are synthesized under the catalysis of PPA [3], such as the cyclization of N-ethoxyformylethyl spirotetrahydroquinoline under the catalysis of excess PPA, the yield is about 60% (formula 2). [3] Used as compound cyclizing agent and acylating agent in organic synthesis. Also used as a substitute for orthophosphoric acid and analytical reagents.
Mostly in below reactions:
Catalyze intramolecular cyclization reaction
Catalyze the intermolecular cyclization reaction
Catalytic molecular rearrangement and isomerization
Please visit below webpage for details:
https://www.panchemica.com/polyphosphoric-acid/